Covid-19: Novel Therapies to the Rescue
On 30 January 2020, the WHO declared COVID-19 a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC). Healthcare scientists have been working diligently to develop therapeutics to combat the contagion, save lives, and reduce the adverse impact on livelihoods. Antivirals, immune modulators, and monoclonal antibodies are key therapies recommended for treating specific COVID-19 infections in hospitalised patients.
Antivirals
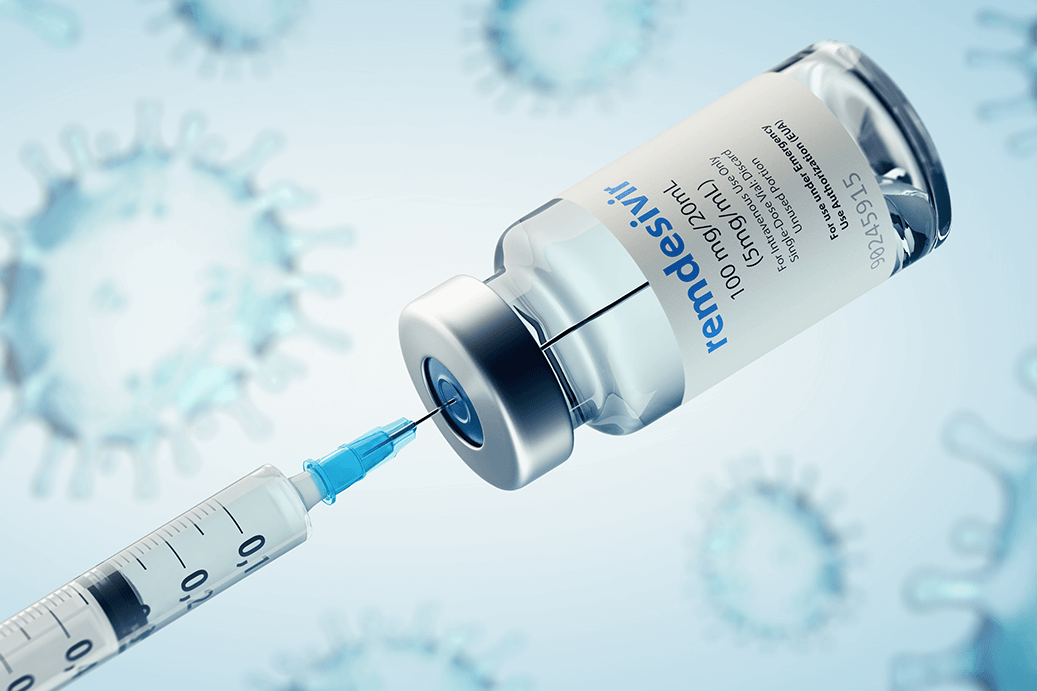
Antiviral drugs, like Remdesivir are prescribed for the coronavirus, given their potential to prevent the infectious agent from invading, reproducing, and proliferating within healthy human cells. Antiviral medicines typically work by blocking host cell receptors, preventing the virus’s attachment protein from binding to the surface molecules of the host cell. Aantivirals prevent the contagion from gaining access to the inside machinery of the cell. Significantly, these drugs delay the infection from progressing within the body. Some antiviral drugs, approved or under evaluation for the treatment of COVID-19 -
|
Remdesivir |
Approved by the FDA for use in hospitalized adults and children (aged 12 years and older) for treatment of Covid-19 |
|
Chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine |
Under evaluation as a preventative treatment for Covid-19 |
|
Amodiaquine |
Generally deemed to be an effective Covid-19 medication |
|
Favipiravir |
Considered a promising antiviral drug that offers benefits like reduced hospital stay and ventilation requirements for patients hospitalized with Covid-19 |
|
ArtesunateLopinavir / ritonavir combination |
|
|
Umifenovir |
|
|
Ribavirin |
|
|
EIDD-2801 |
|
|
Niclosamide |
|
|
Nitazoxanide |
|
|
Oseltamivir |
|
|
Ivermectin |
|
|
AT-527 |
Immune modulators
The immune system’s response to the coronavirus sometimes results in excess secretion of pro-inflammation cytokines (cytokine storm). While such inflammatory action promotes pathogen clearance (an unintended effect), the hyperactive immune response to the pathogen triggers cell deaths, especially in the lungs. This could lead to severe respiratory distress, lower blood oxygen levels, and cause organ failures, and other life-threatening complications. Immune modulator drugs are beneficial in certain severe cases of patients hospitalised with COVID-19 since they help counteract the host cells’ excessive immune response. Some immune modulating drugs administered in moderate doses have reportedly reduced mortality rates of patients with severe COVID-19 conditions.
|
Dexamethasone |
Baricitinib |
Leronlimab |
|
Hydrocortisone |
Ruxolitinib |
LY-CoV555 |
|
Convalescent plasma |
Acalabrutinib |
LY-CoV016 |
|
Budesonide (inhaled) |
Imatinib |
VIR-7831 |
|
AZD7442 |
Brensocatib |
Risankizumab |
|
Azithromycin |
Ravulizumab |
Lenzilumab |
|
Doxycycline |
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin |
IMU-838 |
|
Interferons |
Namilumab |
|
|
Tocilizumab |
Infliximab |
|
|
Sarilumab |
Adalimumab |
|
|
Regdanvimab |
Otilimab |
|
|
Canakinumab |
Medi3506 |
|
|
Anakinra |
Antiviral antibody cocktail |
Monoclonal antibodies
Antigens (chemicals, toxins, pollen portions of a virus or bacteria) urge the body’s immune system to produce antibodies against them as a defense. It is possible to design and replicate copies of antibodies “programmed” to fight off a specific antigen in a lab setting and then discharge them into the bloodstream. A white blood cell, exposed to a certain antigen, can be cloned in the lab to generate a large number of genetically identical copies or monoclonal antibodies (MaBs) capable of counteracting the antigen. An MaB, essentially a human-made protein, could be derived from mice, humans or both. Here are some MABs, authorised for emergency use against COVID-19.
|
Bamlanivimab and etesevimab |
|
REGN-COV2: Casirivimab and imdevimab |
|
Levilimab (Ilsira) |
|
Tocilizumab |
|
Itolizumab |
The production of antiviral drugs, immune modulators, MaBs, and other contemporary Covid therapeutics calls for an enabling infrastructure, comprising stainless steel single-use preparation vessels and fermenter systems. Researchers at DDE have years of experience in manufacturing automated enterprise-class fermenter systems, bioreactor skids, and cross flow skids to promote cell growth and vaccine generation at large, medium, and small bio-pharmaceutical organisations.
